Build a chatbot
Learn how to build a chatbot using our Agent APIs. In this tutorial, we create an onboarding assistant for a manufacturing use case. This chatbot answers employee questions from uploaded documents that contain safety protocols and equipment manuals. This example may provide inspiration for your specific use case.
What you will build
A single-page web app with a clean chat interface, powered by React for the frontend and Vectara's Agent APIs for the backend. The agent uses corpora and web search tools to provide beginner-friendly answers in Markdown format. The application has the following features:
The chatbot will look like this example:
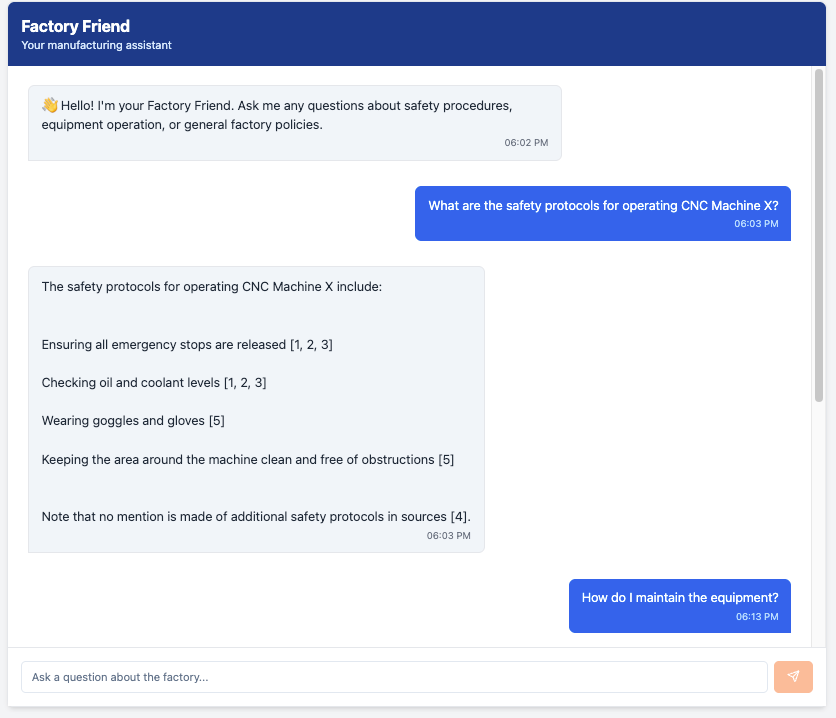
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, ensure you have the following:
- Basic knowledge of React and TypeScript.
- Vectara account: Sign up and get an API key with query and indexing permissions, or use your Personal API key.
- Install the latest releases of Node.js and npm.
This tutorial includes complete instructions for creating a corpus with sample manufacturing data, so no existing data is required.
Chatbot build overview
Follow this process to create the chatbot.
- Set up your Vectara corpus.
- Create an agent with search tools.
- Create a new React project.
- Install required dependencies.
- Create the project structure and components.
- Test your chatbot.
Step 1. Set up your corpus with sample data
Create a corpus and populate it with sample manufacturing data. This example shows you how to create a corpus with the API.
Create the corpus
CREATE CORPUS
Code example with bash syntax.1
Add sample documents
Index sample documents to populate your corpus. Here are example documents you can add:
Safety protocol document
INDEX SAFETY PROTOCOL DOCUMENT
Code example with bash syntax.1
Equipment manual document
INDEX EQUIPMENT MANUAL DOCUMENT
Code example with bash syntax.1
Onboarding guide document
INDEX ONBOARDING GUIDE DOCUMENT
Code example with bash syntax.1
After adding these documents, your corpus will be ready for the agent to search.
Step 2. Create an agent with multiple search tools
Before building the frontend, create an agent that will power your chatbot. This agent will have access to both your corpus and web search as a backup for questions outside your corpus. If you want, you can omit the web search tool and only use the corpora search.
CREATE AGENT WITH MULTIPLE TOOLS
Code example with bash syntax.1
This creates an agent with:
- Corpora search tool: Searches your
acme_onboardingcorpus for company-specific information. - Web search tool: Falls back to web search for general questions, or when the corpus lacks information.
- Smart instructions: The agent knows to try internal documents first, then web search as backup.
- Conversational step: Responds naturally to user input with proper tool selection.
The agent chooses the appropriate tool automatically based on the question. For example:
- "What are the safety protocols for CNC Machine X?" - Uses corpus search
- "What is Six Sigma?" - May use web search if not in your corpus
- "How do I get my ID badge?" - Uses corpus search
Save the agent_key (in this example: factory-friend) for use in your
application.
Step 3. Create a new React project with Vite
INITIALIZE REACT PROJECT
Code example with bash syntax.1
Step 4. Install required dependencies
INSTALL DEPENDENCIES
Code example with bash syntax.1
Step 5. Create the project structure and components
Create the following directory structure:
PROJECT STRUCTURE
Code example with bash syntax.1
Now let's create each file with the proper implementation.
Update global styles
Set up the base styles for the application, including the font family and consistent spacing and button states across all components.
SRC/INDEX.CSS
Code example with css syntax.1
Create the API service
This service manages communication with the Agent API, including session creation, message sending, and error handling. It maintains session state across multiple messages for conversation continuity.
SRC/SERVICES/VECTARAAPI.TS
Code example with typescript syntax.1
Create message types and component
Define the message data structure and create a component that displays individual chat messages.
SRC/COMPONENTS/CHATMESSAGE.TSX
Code example with tsx syntax.1
Create input component
Build a text input component with a send button that handles message submission, input validation, and disabled states during API calls.
SRC/COMPONENTS/CHATINPUT.TSX
Code example with tsx syntax.1
Create chat container
Assemble the main chat interface that manages message state, handles sending and receiving messages through the API service, and orchestrates the header, message list, and input components.
SRC/COMPONENTS/CHATCONTAINER.TSX
Code example with tsx syntax.1
Create API key form
Build a simple form component that prompts users to enter their Vectara API key before accessing the chatbot. This handles input validation and submission.
SRC/COMPONENTS/APIKEYFORM.TSX
Code example with tsx syntax.1
Create main page
Create the main application page that manages API key storage in localStorage
and conditionally renders either the API key form or the chat interface.
SRC/PAGES/INDEX.TSX
Code example with tsx syntax.1
Create App component
Define the root application component that renders the Index page.
SRC/APP.TSX
Code example with tsx syntax.1
Update main entry point
Set up the React application entry point that mounts the App component to the DOM with StrictMode enabled for development warnings.
SRC/MAIN.TSX
Code example with tsx syntax.1
Step 6. Run and test your chatbot
Start the development server:
START DEVELOPMENT SERVER
Code example with bash syntax.1
Step 7. Test your chatbot
To verify your chatbot works:
- Open the app in your browser (for example:
http://localhost:5173after runningnpm run dev). - Enter your Vectara API key when prompted.
- Try these sample questions:
Questions that should use corpus search:
- "What are the safety protocols for operating CNC Machine X?"
- "How do I maintain the equipment?"
- "What is the onboarding process for new employees?"
- "What PPE do I need in the machine shop?" Questions that will probably use web search (data not in corpus):
- "What is Six Sigma methodology?"
- "What are the latest ISO manufacturing standards?"
- "Who invented the assembly line?"
- Check that responses include Markdown formatting (numbered lists, citations).
- Verify the agent correctly chooses which tool to use based on the question.
- Test the conversation history - sessions maintain context across messages automatically.
You can upload your own data and test the agent responses, and use other agent tools.
Move your chatbot to production
Production environments introduce new requirements for reliability, security, scalability, compliance, and maintainability. After building and validating your chatbot with the Vectara Agent API, take additional steps to prepare your application for production use.
This section highlights key changes from the tutorial environment and provides tips in a real-world environment. Here is a summary of the key changes:
- API security: Move secrets out of source code and implement secure storage and transmission for API keys.
- Error handling & monitoring: Add advanced error handling, logging, and real-time monitoring.
- Scalability: Optimize for concurrent usage, rate limits, and backend scaling.
- Authentication and authorization: Implement user authentication and RBAC.
- Environment management: Use environment variables and configuration files for deployment environments.
- Compliance: Address privacy, audit, and compliance requirements relevant to your organization, such as SOC2.
- Testing and quality: Add integration, unit, and load testing for critical workflows.
- Deployment: Automate build, test, and deployment processes.
- Observability: Instrument the app for metrics, tracing, and alerting.
- Internal documentation: Update onboarding, support, and maintenance documentation for internal teams.
Secure API keys and configuration
Instead of manually inputting API key or storing in localStorage:
- Store API keys and secrets in a secure vault, such as AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, or HashiCorp Vault.
- Never expose API keys to the client and browser.
- Route all API traffic through a backend to enable API key protection, rate limiting, and custom business logic such as query postprocessing.
- Use
.envfiles and server-side environment variables for secrets and sensitive configuration.
Error handling and logging
Instead of basic logs and inline error messages:
- Implement centralized logging.
- Send application errors and unhandled promise rejections to an observability service.
- Mask sensitive information in logs.
User authentication and access control
Instead of opening the chatbot to all visitors:
- Integrate authentication, such as OAuth2, SAML, Auth0, Okta, Azure AD.
- Implement authorization rules for different user groups.
- Restrict access to chat or sensitive endpoints as appropriate.
Environment-specific configuration
Instead of hardcoding the configuration in source files:
- Move all environment-dependent values (API endpoints, agent keys, feature flags) to environment variables or configuration management tools.
- Support separate configurations for development, staging, and production environments.
Test for quality
Instead of manual browser tests:
- Add automated testing through unit tests, integration tests, and load/stress tests.
- Add a CI pipeline to enforce testing and code quality.
CI/CD and automated deployments
Instead of manual npm run dev and local-only builds:
- Use a CI/CD tool to automate build, test, and deployment steps.
- Deploy to cloud infrastructure (Vercel, Netlify, AWS, Azure, GCP) or internal servers.
- Maintain separate environments for staging and production.
Metrics and alerts
Instead of having no monitoring or alerting:
- Set up your backend and frontend for metrics (API response times, error rates, user activity).
- Use an APM solution for tracing and health checks.
- Set up alerts for failures and performance regressions.
Compliance
- Document data retention policies and then enforce these policies.
- Implement audit logging for user interactions with sensitive data.
- Ensure you meet internal and external privacy and compliance standards.
Documentation and support
- Create internal documentation for deployment, monitoring, and support processes.
- Provide user-facing help and troubleshooting guides.